Multimodal Diffusion for Self-Supervised Pretraining
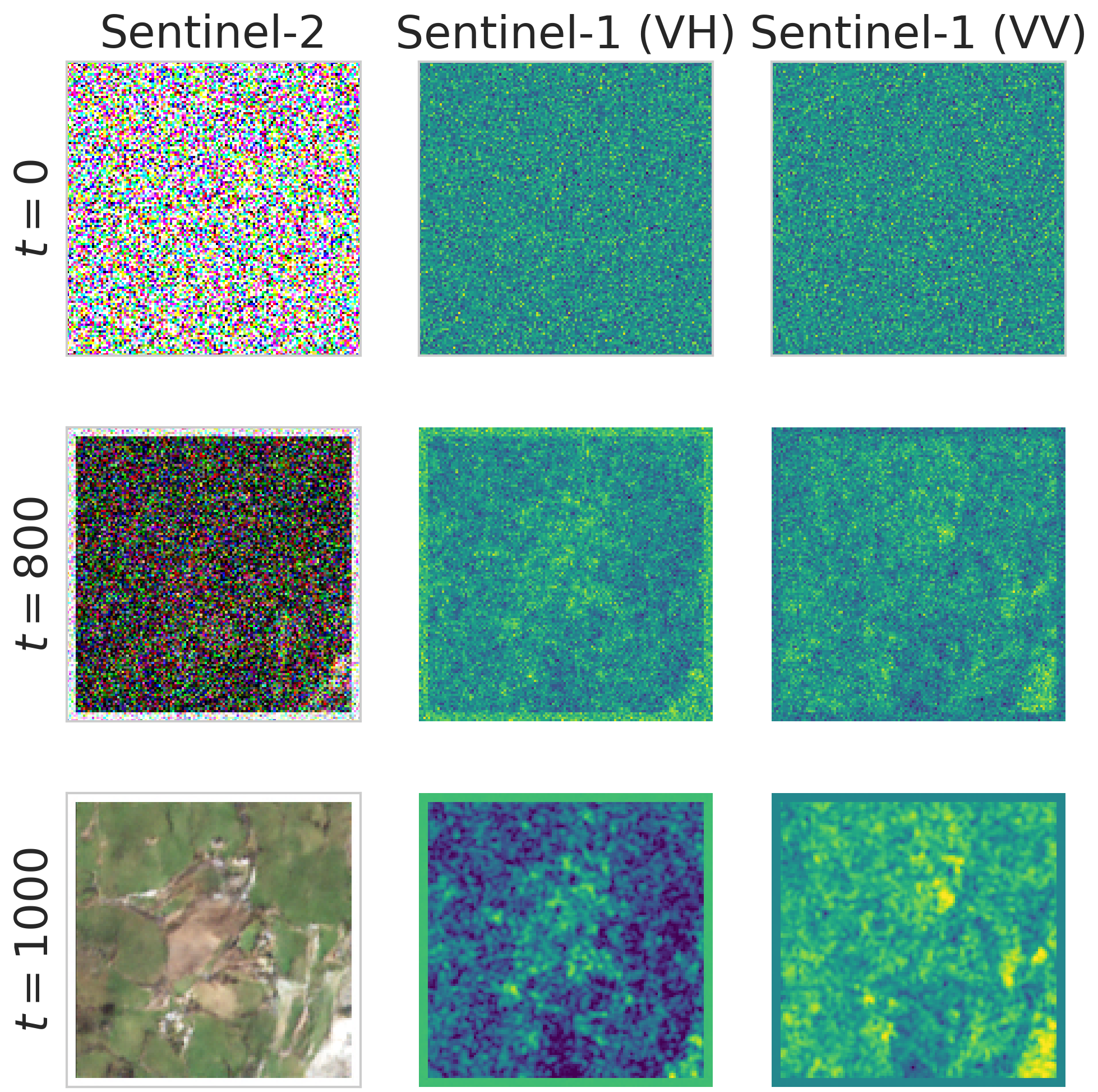
Deep learning models based on diffusion processes have shown great potential in a range of generative tasks, such as image generation. For remote sensing applications, generative models are not that common. The question that we tried to answer is whether diffusion processes can be used to efficiently pretrain models for discriminative tasks?
read moreBen-Ge - Extending Bigearthnet with Geographical and Environmental Data
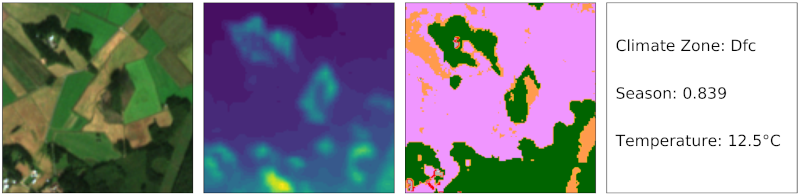
Multimodal datasets for remote sensing are oftentimes limited to two data modalities, such as multispectral and SAR polarization data. In order to experiment with a much wider range of data modalities, we extended the well-known BigEarthNet dataset to includes a wide range of data modalities.
read moreTraffic Noise Estimation from Satellite Imagery with Deep Learning
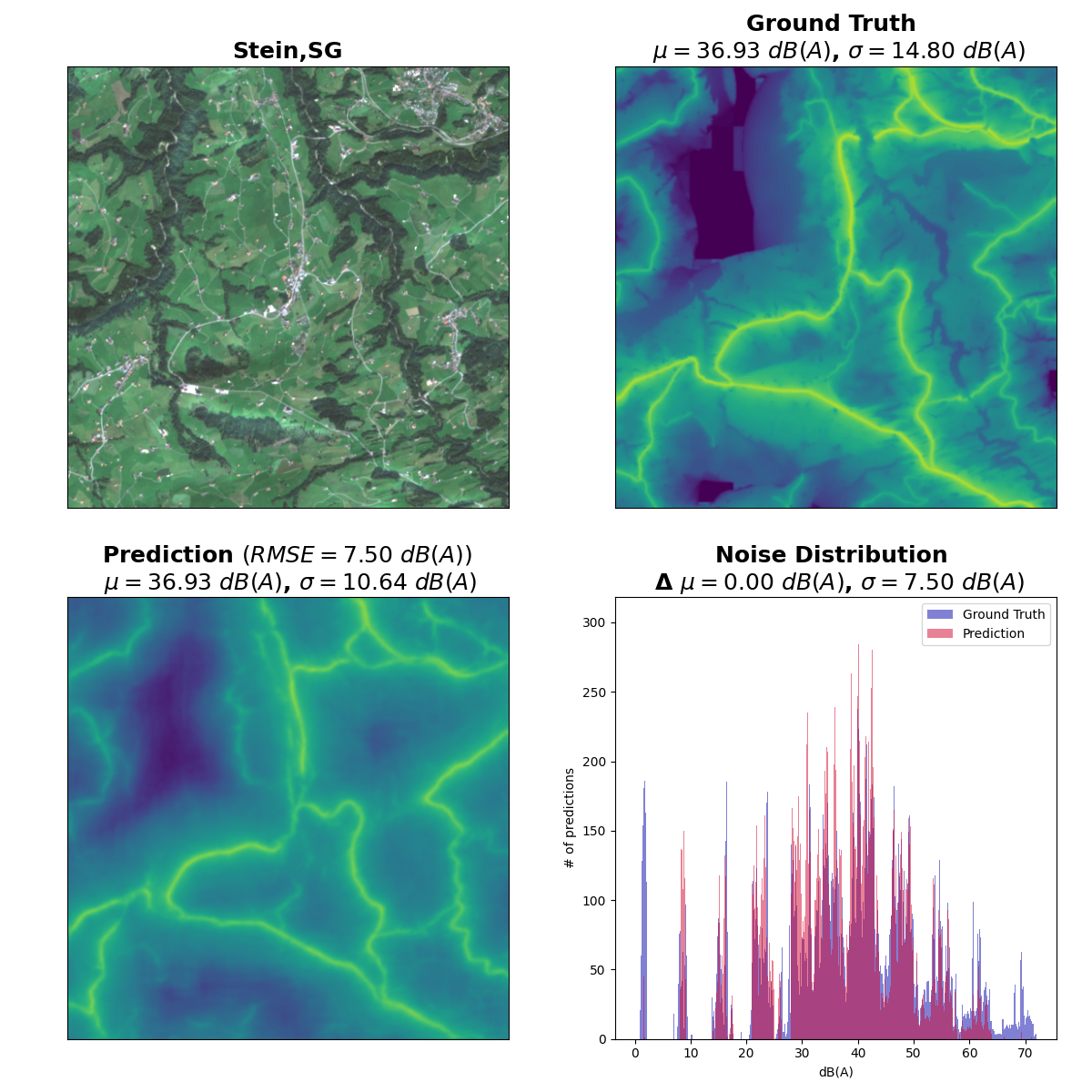
Road traffic noise is a global issue that can lead to severe health effects. Despite the ubiquity of traffic noise, its quantification or estimation is complicated and detailed road traffic maps are only available for select countries or areas. We investigate whether it is possible to train a segmentation model to esimate road traffic noise from satellite imagery.
read moreContrastive Self-Supervised Learning for Multi-modal Earth Observation Data
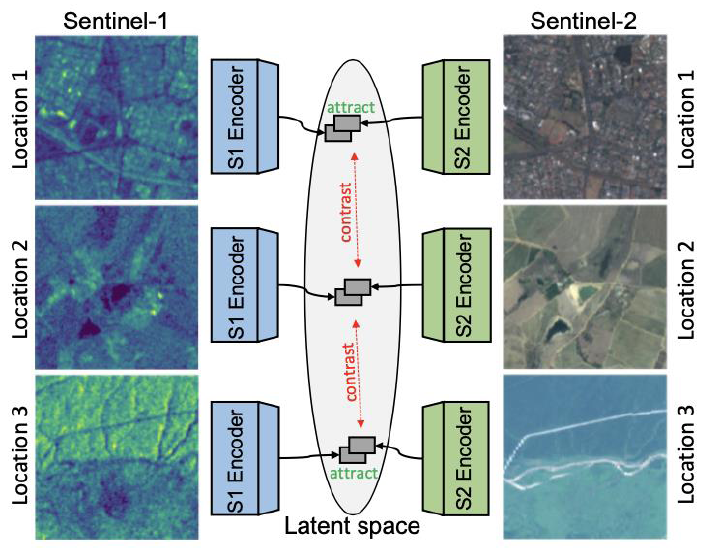
Self-supervised learning provides a powerful means to pretrain models based on un-labeled data. Un-labeled Earth observation data are abundant: this circumstance combined with the availability of multi modal data makes Earth observation a perfect playground for self-supervised learning. Our early results are very promising…
read moreEstimating Power Plant Greenhouse Gas Emissions from Satellite Imagery
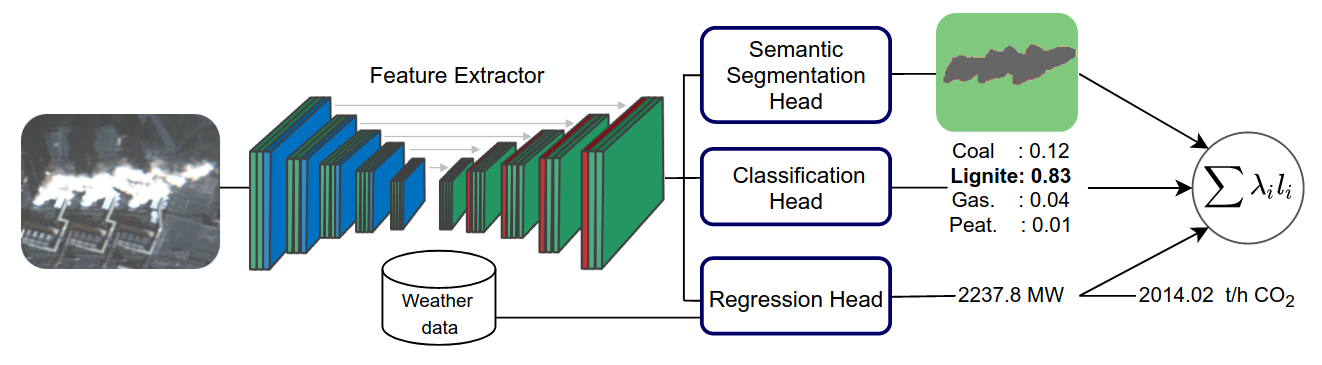
Tracking Greenhouse Gas emissions will be increasingly important in the future, as power generation from fossil fuels is supposed to fade out. Independent tools to monitor power plants are required for this task. We present a method that uses freely available satellite imagery to estimate power generation and CO2 emission rates on a global scale.
read moreEstimation of Surface Level NO2 from Remote Sensing Data
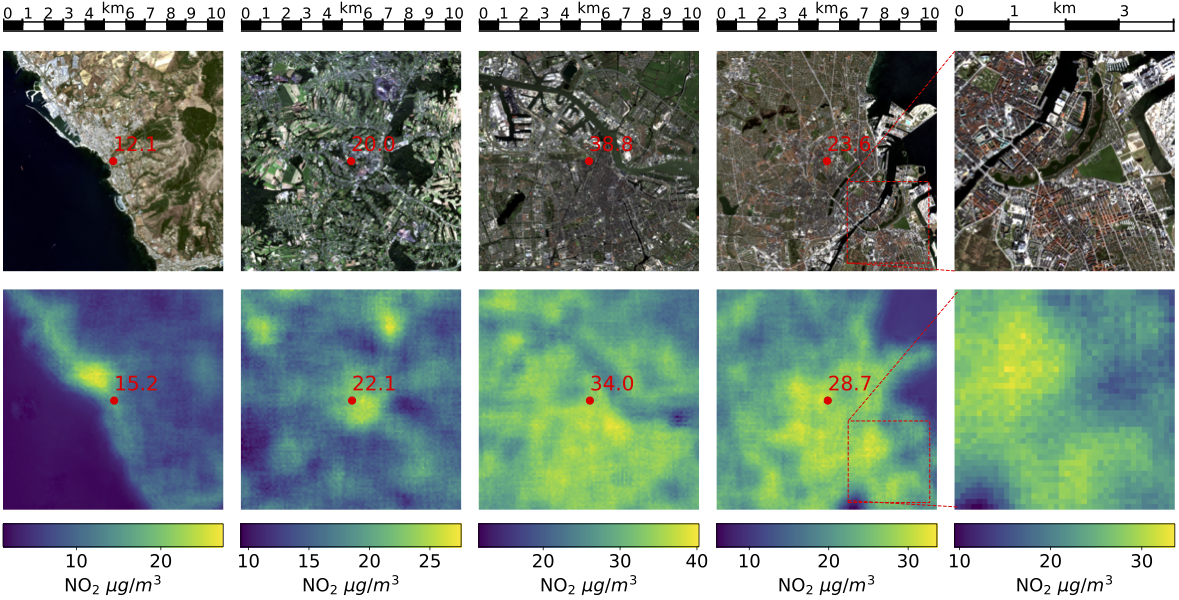
Air pollution is a major health issue and often also contributes to climate change. Measuring air pollution is costly and therefore only available in some countries. We investigated whether freely available Earth observation data can be utilized to estimate air pollution on the surface level.
read moreCommercial Vehicle Traffic Detection from Satellite Imagery with Deep Learning

Can we identify trucks from space and estimate truck traffic rates anywhere on the planet? Yes, we can!
read morePower Plant Classification from Remote Imaging with Deep Learning

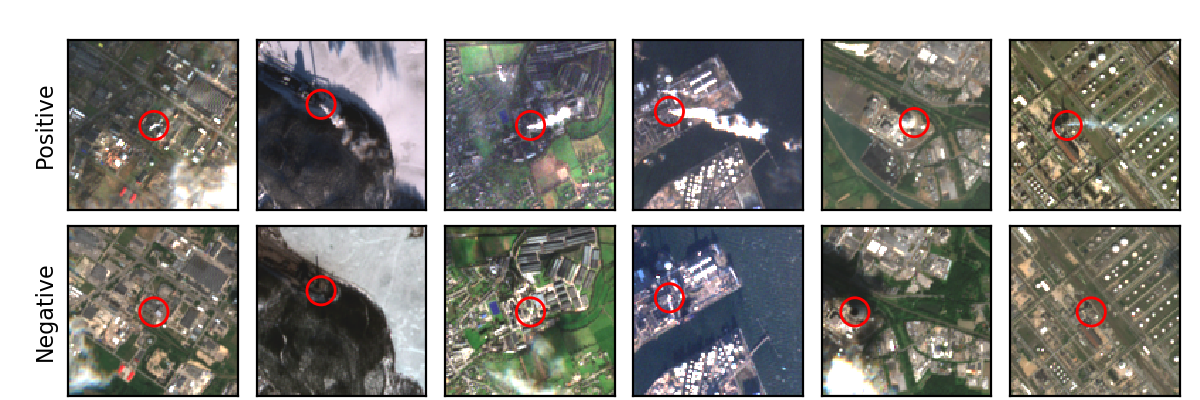
We developed a deep learning model that is able to distinguish between
10 different types of power plants in an effort to automatically identify
and characterize industrial sites in satellite imagery. This work will
help us to estimate greenhouse gas emission rates for individual industrial
sites in the future.
read moreCharacterization of Industrial Smoke Plumes from Remote Sensing Data

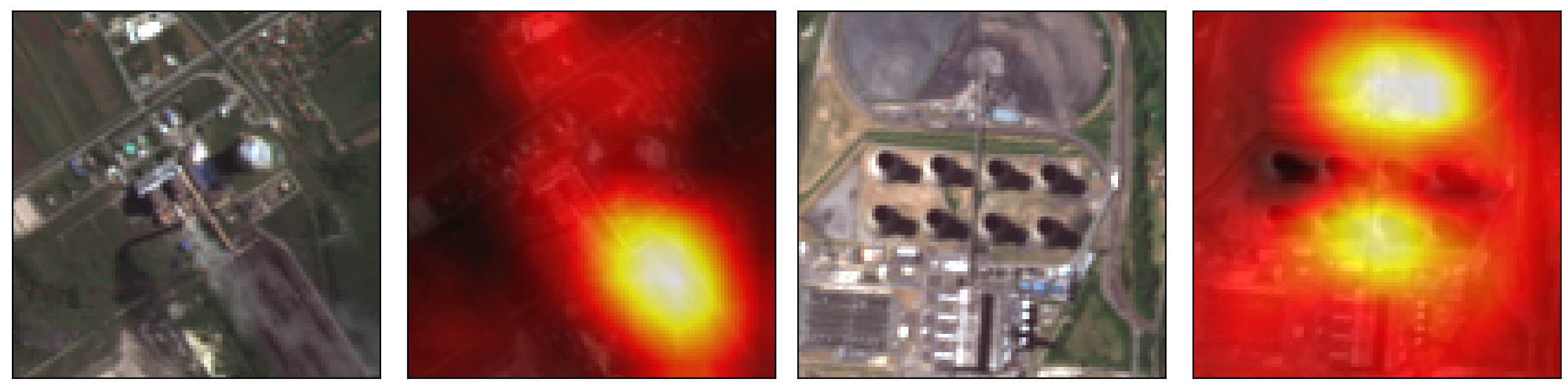
Greenhouse gas emissions from the industrial economic sector are
a major driver of the currently observed climate change. We developed
a deep learning approach to identify and characterize industrial
smoke plumes. In the future, we will utilize this approach to estimate
greenhouse gas emissions from remote sensing data on a global scale.
read moreDon Quixote and the Dormant Comets - My Astronomical Legacy
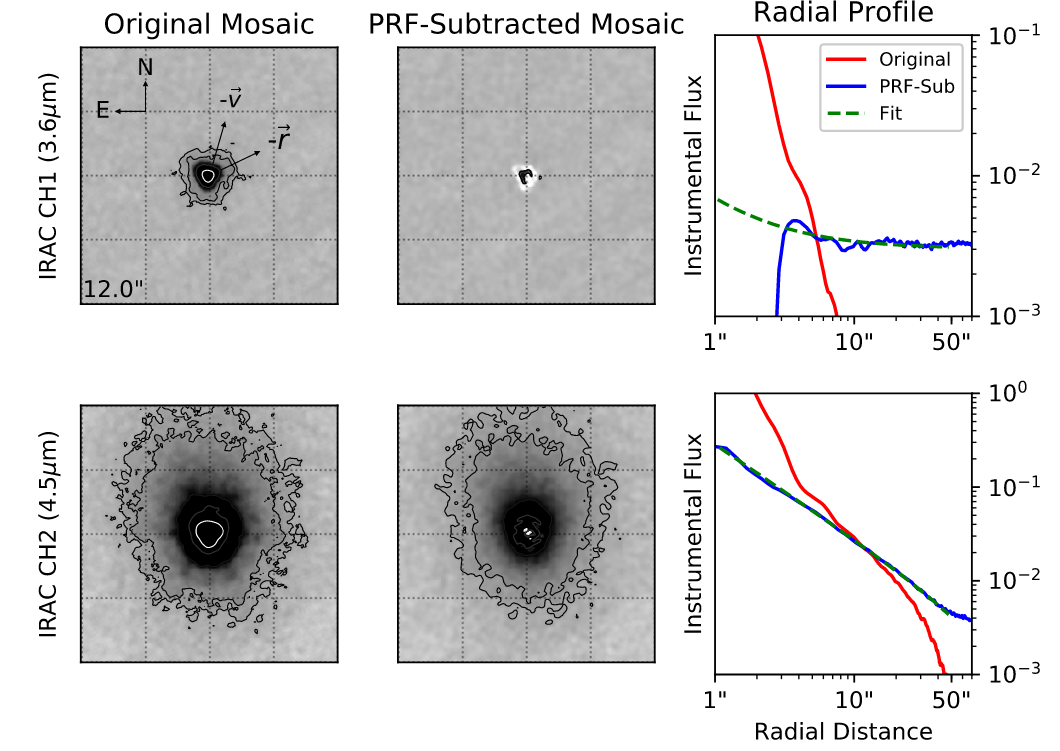
Don Quixote has been considered asteroidal since its discovery in 1983,
despite its comet-like orbit. We found activity in this object during
its 2009 and 2018 apparitions, leading us to believe that it really
is an active comet. But are there other objects like Don Quixote? I
monitored a sample of ~100 asteroids that are somewhat likely to turn
active, too, over a period of more than 4 years. Bottom line: Don Quixote
is rather unique.
read moreAutomated Cloud Detection with Machine Learning
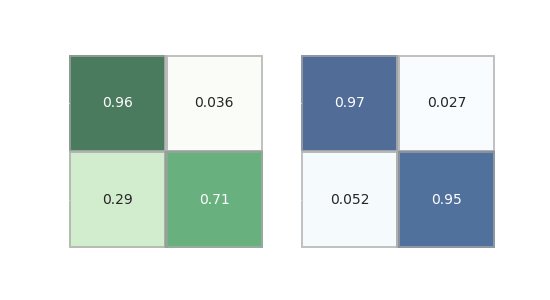
This is a toy project that turned into a real research project and a preparation
for my new job as
research scientist in computer vision: using machine
learning techniques to identify clouds in all-sky camera images.
read moreSpitzerNEOs - Diameters and Albedos for 2132 Near-Earth Objects
Based on Spitzer Space Telescope observations, we derived diameter and
albedo estimates for 2132 asteroids in near-Earth space - the largest
dataset of its kind. Our results and data are available online.
read moreA plethora of asteroids in TESS data

TESS is a satellite that observes bright stars to find brightness
modulations revealing exoplanet transits - but it also observes
a lot of asteroids over a long period of time, which makes it a unique
asset for deriving long asteroid rotation periods.
read moreAsteroid Shape Information from Gaia DR2
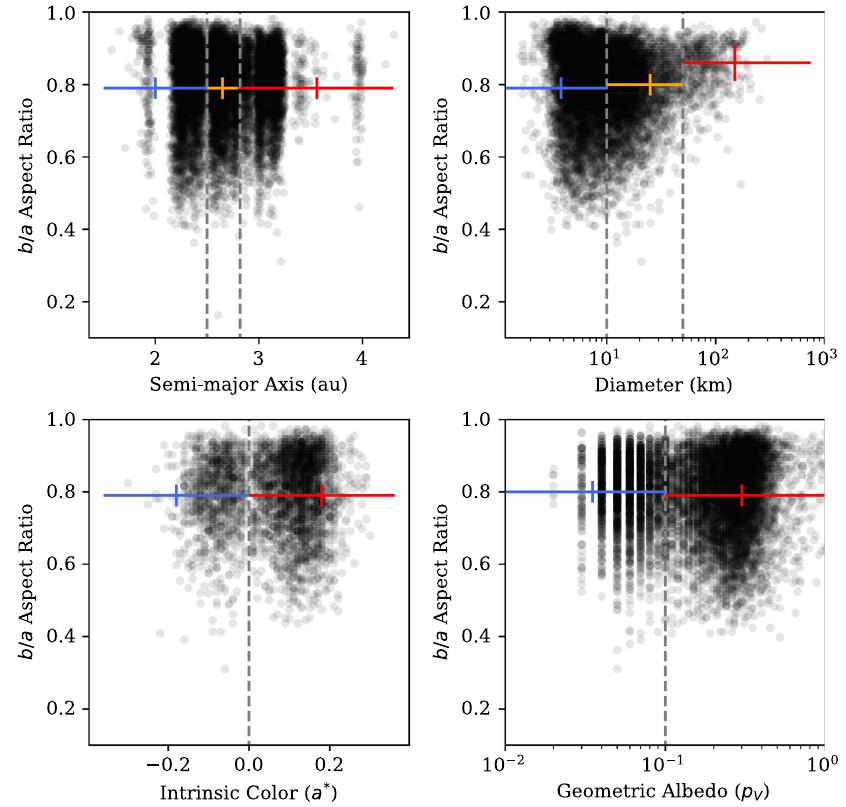
The Gaia mission builds a unique survey of the stars in our Milky Way - but
it also observes asteroids that are crossing its field of view. We derive
ensemble shape information for different asteroid populations from the
first batch of asteroid data from Gaia.
read moreAre there Limits on the Applicability of Asteroid Thermal Models for Near-Earth Asteroids?
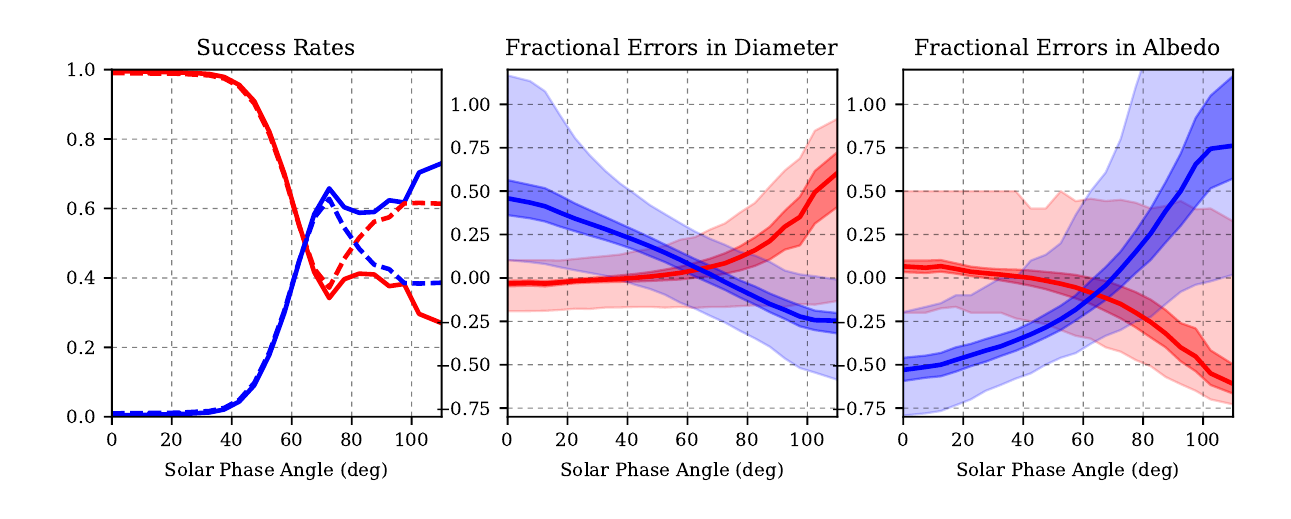
There is a range of asteroid thermal models that are based on different
physical assumptions. In this analysis, I investigate how these assumptions
affect their results and applicability to different situations.
read moresbpy - A Python module for small-body planetary astronomy
sbpy is an astropy affiliated package for small-body planetary astronomers.
We proposed this idea to NASA and were funded for developing this Python
module, which is outlined here.
read morePhotometrypipeline
photometrypipeline is a Python software package for automated image
registration, calibration, and extraction of photometry tailored to the
needs of asteroid observer. However, pp can also be applied to other
imaging observations.
read moreHow many Dead Comets are there?
Dead comets are small bodies that appear as inactive asteroids, but have
a cometary origin. Some of these objects might still harbor ices and can
still activate and appear comet-like. Since these objects might signifcantly
contribute to the volatile reservoir of the asteroid population, it is
important to understand how many of these objects there are.
read moreRapid-Response Spectrophotometric Observations of NEOs with UKIRT and RATIR
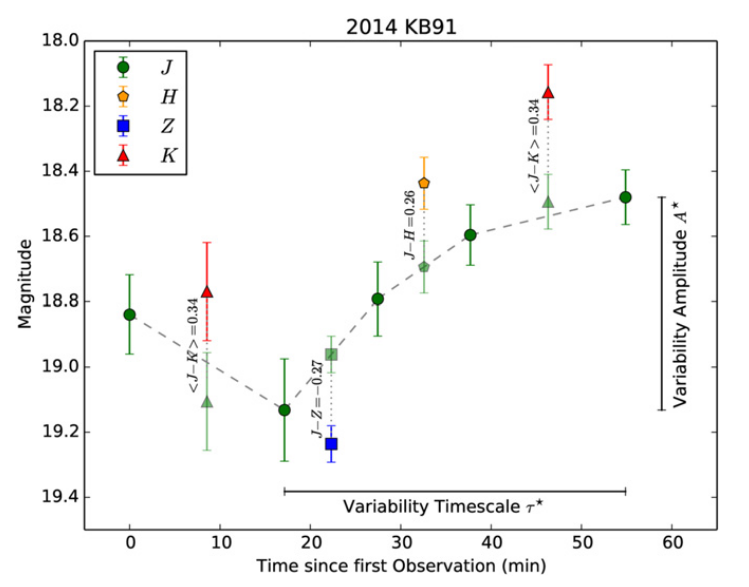
With rapid-response observations using UKIRT, we are able to observe newly
discovered near-Earth asteroids when they are still close to Earth and
thus bright. Our observations enable a probabilistic taxonomic
classification of asteroids with typically small sizes and the determination
of their compositional distribution.
read morePhysical Properties of two tiny Asteroids from Spitzer Observations
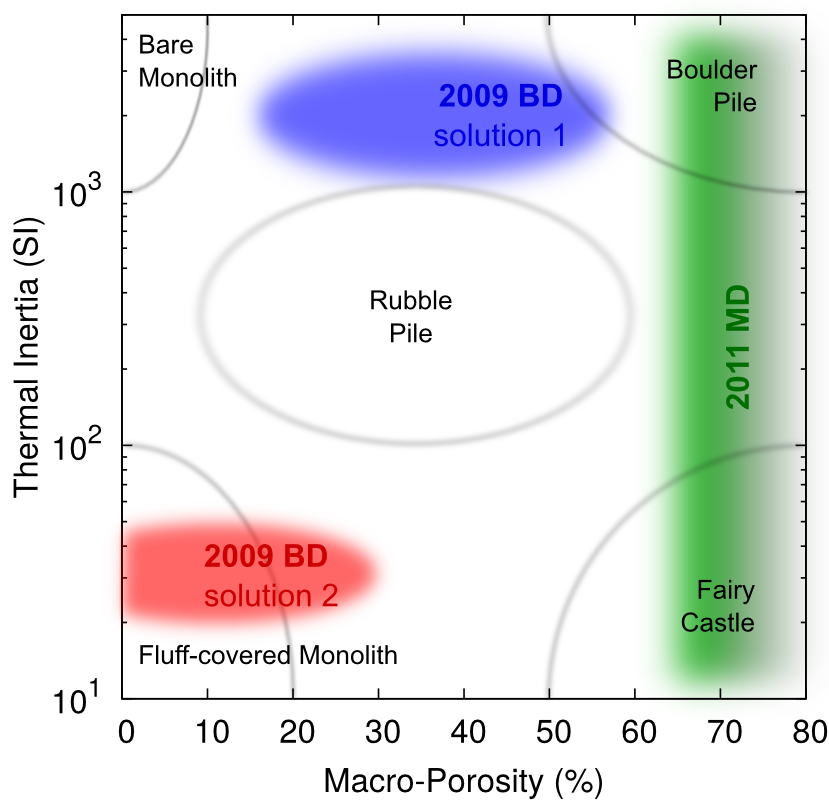
We observed two very small asteroids with the Spitzer Space Telescope to
actually measure their physical properties for the first time. The
constraints that we were able to place on their properties do not agree
with the standard picture of small asteroids.
read moreDetection of Cometary Activity in NEO Don Quixote
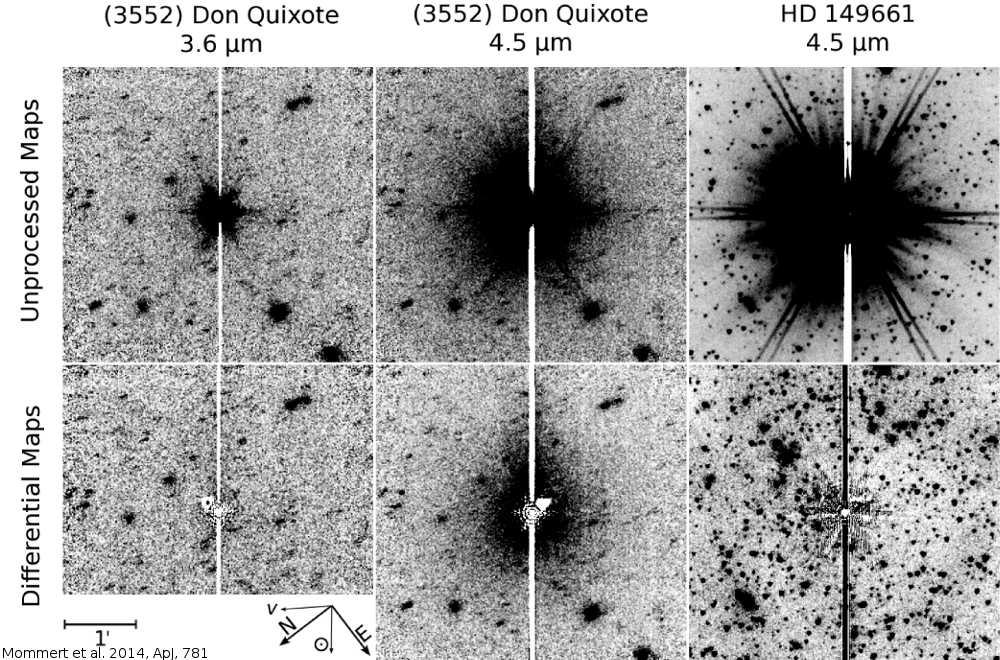
Near-Earth asteroid Don Quixote has long since been considered a good
candidate for an inactive comet nucleus due to its comet-like orbit. Since
its discovery in 1983, comet-like has never been observed - until we
observed this object with the Spitzer Space Telescope…
read moreHerschel Observations of Plutinos
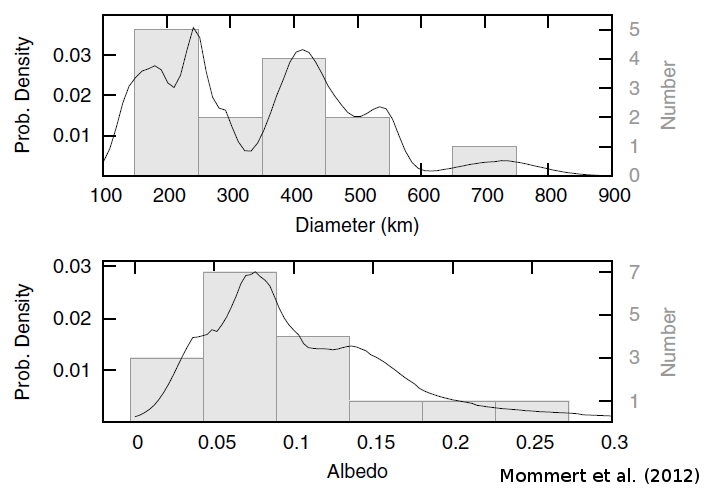
My first research paper. Using Herschel Space Observatory observations,
we investigated the physical properties of 18 Plutinos - small bodies at
the outskirts of the Solar System that have orbital properties similar to
those of Pluto. What we found? That Pluto is pretty unique…
read more